About me
Like many other Jekyll-based GitHub Pages templates, academicpages makes you separate the website’s content from its form. The content & metadata of your website are in structured markdown files, while various other files constitute the theme, specifying how to transform that content & metadata into HTML pages. You keep these various markdown (.md), YAML (.yml), HTML, and CSS files in a public GitHub repository. Each time you commit and push an update to the repository, the GitHub pages service creates static HTML pages based on these files, which are hosted on GitHub’s servers free of charge.
Many of the features of dynamic content management systems (like Wordpress) can be achieved in this fashion, using a fraction of the computational resources and with far less vulnerability to hacking and DDoSing. You can also modify the theme to your heart’s content without touching the content of your site. If you get to a point where you’ve broken something in Jekyll/HTML/CSS beyond repair, your markdown files describing your talks, publications, etc. are safe. You can rollback the changes or even delete the repository and start over – just be sure to save the markdown files! Finally, you can also write scripts that process the structured data on the site, such as this one that analyzes metadata in pages about talks to display a map of every location you’ve given a talk.
- Register a GitHub account if you don’t have one and confirm your e-mail (required!)
- Fork this repository by clicking the “fork” button in the top right.
- Go to the repository’s settings (rightmost item in the tabs that start with “Code”, should be below “Unwatch”). Rename the repository “[your GitHub username].github.io”, which will also be your website’s URL.
- Set site-wide configuration and create content & metadata (see below – also see this set of diffs showing what files were changed to set up an example site for a user with the username “getorg-testacct”)
- Upload any files (like PDFs, .zip files, etc.) to the files/ directory. They will appear at https://[your GitHub username].github.io/files/example.pdf.
- Check status by going to the repository settings, in the “GitHub pages” section
Research Interests
- Information Retrieval
- Natural Language Processing
- Neural Indexing
Updates
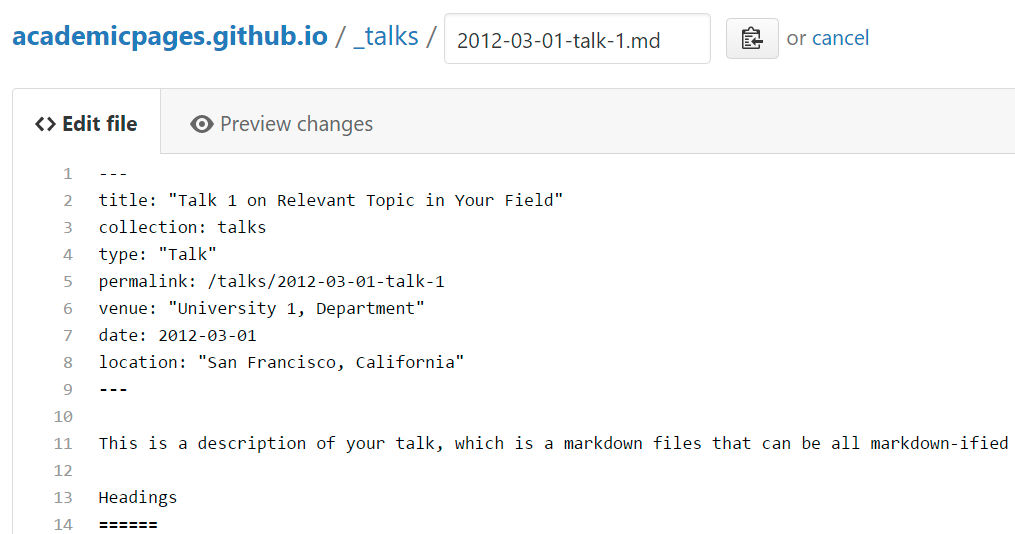
Many people use a git client to create files on their local computer and then push them to GitHub’s servers. If you are not familiar with git, you can directly edit these configuration and markdown files directly in the github.com interface. Navigate to a file (like this one and click the pencil icon in the top right of the content preview (to the right of the “Raw | Blame | History” buttons). You can delete a file by clicking the trashcan icon to the right of the pencil icon. You can also create new files or upload files by navigating to a directory and clicking the “Create new file” or “Upload files” buttons.
Example: editing a markdown file for a talk